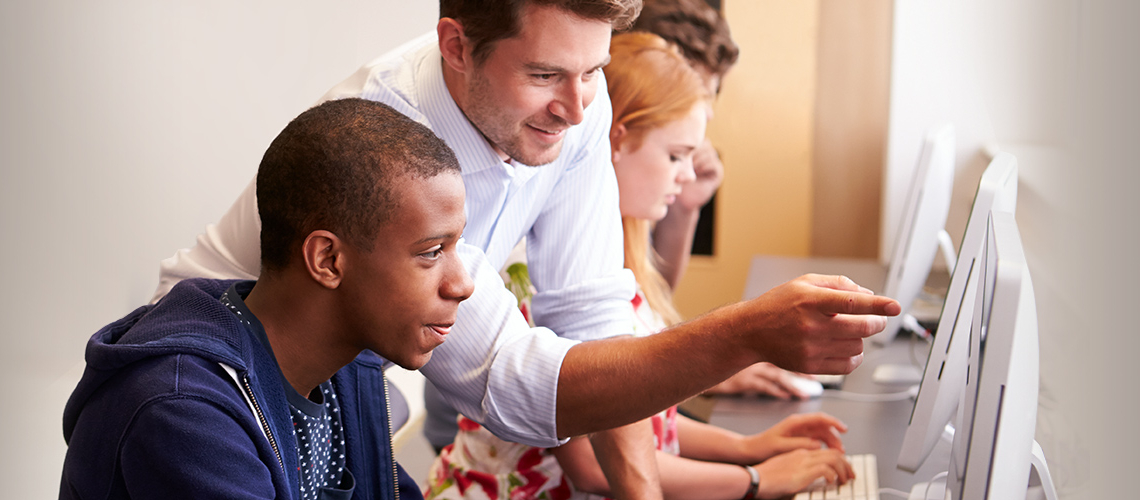
The need to adapt learner instruction to the challenges society gives us has increased in recent years. What schools used to teach students, the skills needed in the past and their applicability in real life are no longer suitable in a scientifically and technologically developing world.
In most schools across the globe, students leave their classrooms only with the tools teachers provide them, and with the knowledge and skills they acquire throughout their development. Well, that's not enough anymore! Educators and learners have started to realize that the traditional teacher input and student reproduction of information could no longer ensure learners' successful transition from students to active citizens contributing to the labor market.
In a quest to find solutions to these issues, educators and experts in the field have tried to find an approach to learning that would spark students' curiosity and motivation, that would engage them more in class and which would provide them with a set of skills necessary to face the 21st century society.
Authentic learning came as a constructivist approach to teaching in which learners are active participants in their own instruction that allows for the acquisition of new concepts and skills oriented towards real-life applicability.
9 Characteristics of authentic learning
So far, there hasn't appeared any model of authentic learning that can be used as a pattern worldwide, hence educators have to adapt their interpretations of the approach to suit their students' needs. Nevertheless, experts in the field have mentioned some common features:
- Real world applicability of tasks
- Interdisciplinary learning
- Student-directed learning
- Open-ended inquiry
- Exploration and collaboration
- Community discourse
- High-order thinking
- Mastery of key concepts
- Flexibility of learning environment and resources
Let’s explore these a little:
1. Real world applicability of tasks
Having students solve tasks reflected in real life increases students' motivation and provides them with knowledge that is meaningful outside the classroom. By doing so, students learn the relevance of what they are studying. With authentic learning students can make informed career choices, being better prepared for life after school. Moreover, learning through solving real-life problems, students retain information better because they are able to understand it better and this translates into successful transfer of information from the learner to the future worker.
2. Interdisciplinary learning
This feature is one of the most important aspects of authentic learning in which students interpret one problem by directing it through multiple layers often related to various fields of study. This method provides students a chance to analyze situations from different perspectives and make an informed decision upon the possible solutions.
3. Student-directed learning
Authentic learning focuses on just that: learning. Not teaching. The teacher is merely the facilitator, the guide, providing the learner with well-thought tasks and concepts they need in order to be effective problem-solvers and to gain skills they can use in real life. Since learners have to engage with tasks and situations they are either familiar with or not, sooner or later they realize they might need the knowledge that derives from them, so they stay motivated to learn. What's more, they even take ownership of their learning and get involved in everything the process implies: setting the tasks, the problem-solving process, the learning environment and resources, and the assessment stage.
4. Open-ended inquiry
Any given task requires students to reach a conclusion or a solution. With authentic learning there is no predetermined outcome. Students can come up with different solutions that can be probed by a variety of means. And this is the beauty of this approach. Students work with dedication knowing that there is more than one possible answer, which even the teacher might not know. In these latter contexts, teachers model the behavior a learner should have, making students feel more comfortable with not knowing and changing this phrase into not knowing yet.
5. Exploration and collaboration
When mimicking real life situations, students have to solve tasks usually designed to be tackled in groups. This develops their teamwork skills, such as team-spirit, collaboration and leadership. Students learn how to give instructions, explanations, arguments and justifications. By showing other groups their findings, they open the door towards collaborative feedback, which adds ability to adapt and adjust to the list of skills students develop through learning, which is a process in itself, not an end product.
6. Community discourse
The feedback students receive from their classmates is valuable, but not enough. By exposing their findings to a larger audience, like students from other classes or even members of the community, they will treat more seriously their inquiry and they will have to show their ability to persuade as well, by justifying their conclusions. By receiving the community's response to their work, students feel like their work is important and can benefit society, not only their academics.
7. High-order thinking
Critical thinking is developed in this approach, also, as a variation of design thinking, meaning students have to analyze the task at hand, then they have to gather information and synthesize it, then they have to design a solution or a product, then they materialize it and evaluate it. These actions contribute enormously to students' achievement and their advocacy since they are an intrinsic part of the work environment.
8. Mastery of key concepts
The main purpose of applying authentic learning in schools is to motivate students to surpass standards and be able to evaluate their own learning. Real-life skills are acquired through mastery of key concepts and the ability to apply them in the process of problem-solving. While doing this, students also become aware of their own learning level and are capable of self-evaluation which is necessary when reflecting upon their own results.
Free White paper: Reshaping how students learn using competency-based learning - and how an LMS can support this
9. Flexibility of learning environment and resources
Students become so involved in their education that they can even influence their learning environment. Together with their teachers, they can rearrange the classroom, they can choose different devices for learning, they can opt for flexible seating and they can even select their own resources in their quest for solutions. In this way, students feel more independent, more self-sufficient and more resourceful.
Read more: Smart classroom furniture for the 21st century students
What to remember about authentic learning
To my own understanding, authentic learning is a student-centered approach in which learners act towards their own development, having their own values and expectations and experiencing learning as a reality-grounded process.
Because it involves all four domains of learning — cognitive, affective, psycho-motor and psycho-social — and because the central idea is learning through doing, authentic learning has been portrayed in different approaches over the years, more known to teachers, like project-based learning, simulation-based learning, inquiry-based learning and peer-based assessment, which promote the same core values focusing on the applicability of knowledge outside of the classroom walls.